Cable thermocouples can be thermally coupled to the medium for temperature measurements in vessels and pipelines both in contact with the medium and via an immersion sleeve. The stainless steel sleeve (316L or 316TI) enables use in drinking water, but also in aggressive media.
Use in moisture-critical applications under a wide range of ambient conditions is particularly demanding. Therefore, these cable probes must be specially designed and manufactured.
Cable thermocouples are specially and elaborately qualified and supplied by us with a certificate of suitability.
In this guide, we have compiled information on what you should pay attention to when selecting, purchasing, installing and operating your cable thermocouple.
What is a cable thermocouple?
Thermocouples are thermoelectric sensors with two wires made of different materials. These are connected to each other at one point (measuring point) and one can measure a thermoelectric voltage at their ends (reference junction), which also changes when the temperature changes. This thermoelectric effect is also called Seebeck effect.
Thermocouples measure the temperature difference between the measuring point and the reference junction, i.e. the temperature at the reference junction must be known.
Like platinum sensors, thermocouples are also standardized and can be immersed regardless of the manufacturer. They also have a very fast response time and can be used at very high or very low temperatures. They are inexpensive and come in many different types. Thermocouples also have disadvantages: they are more sensitive than resistance-based temperature probes. Their characteristic curve is not linear. The measuring principle should be known to the user to avoid measuring errors.
How does a cable thermocouple work?
A thermocouple consists of two wires that are made of different materials. This is very important because the different materials also behave differently, creating a measurable thermoelectric voltage when you connect the two wires at one end. This thermoelectric voltage changes when the temperature changes. This effect is named after its discoverer - Seebeck effect.
Unlike resistance-based temperature probes, the temperature difference between the measuring point and the reference junction is determined. The temperature at the reference junction must therefore be known. Therefore, a resistance-based temperature sensor is often installed there. The advantage of thermocouples is that the measuring point and the reference junction do not have to be located next to each other and that the temperature is not "falsified" by line resistances. This means that the measuring tip can be inserted into the process, where it can be very hot, for example - but the temperature is determined at the reference junction.
What are the types?
Cable thermocouples differ in the different alloys from which the thermocouple wires are made. Based on these materials, different characteristics and measuring ranges can be mapped.
You can buy the following material pairings in our online store:
- Iron / Copper-Nickel (Fe/Cu-Ni) = Thermocouple Type J
- Copper / Copper-Nickel (Cu/Cu-Ni) = Thermocouple Type K
We mark the thermocouples according to the IEC 60584-1 standard.
The exact measuring ranges of our thermocouples as well as the characteristic curves can be found in the operating instructions for each probe or in our download area.
What are the different types?
You can find cable thermocouples as Type J and Type K with four different cables.
With these probes, you can determine which length of protection sleeve you need and thus determine the immersion depth for these probes. We offer the following lengths (in mm):
30, 40, 50, 60, 100, 200.
When measuring temperature in solids or when the probe is mounted in an immersion sleeve, the air surrounding the probe slows down the heat conduction from the medium to the probe. This also slows down the temperature measurement and, in extreme cases, leads to incorrect temperature readings. Therefore, please make sure that the temperature probe is thermally coupled to your measuring medium in the best possible way, i.e. select the sleeve diameter so that the air gap is as small as possible.
We offer the following diameters (in mm) depending on the cable material:
3, 4, 5, 6
Choose your cable length:
1 m, 2 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m, 10 m, 15 m, 20 m
What do I need to look out for when making the right choice?
The correct selection depends on your measuring task and the associated requirements for the temperature probe. We often hear questions like:
- Is the probe also compatible with?
- Which thermocouple should I choose?
- Can I change my thermocouple?
- Which cable do I need or even can I replace the cable?
Answering the following questions can help you with your selection:
-
Which type do you need?
Select the required type in the category.
-
What is the right thermocouple for me?
The choice of the thermocouple depends on the one hand on which measuring device you want to use the thermocouple. Please check which thermocouple is to be used according to the technical data or the operating instructions of the measuring device. The different types of thermocouples are not compatible with each other and also have different characteristic curves. You can find an overview of the characteristic curves of our thermocouples here. -
Does the thermocouple fit your measuring range?
In addition to the measuring device, please also check in which measuring range and with which accuracy / tolerance you want to use the thermocouple. Information on the measuring range and tolerance can also be found in the characteristic curves and in the operating instructions for each probe. With thermocouples, it is particularly important to adhere to the measuring range, because if the limit is exceeded, the metal alloy can be irreversibly damaged and then the thermocouple will no longer measure within the specified tolerance range. -
How do I connect it? Should I use a thermocouple cable or a compensating cable?
Thermocouples are connected to the reference junction. By using thermocouple cables or compensating cables, the reference junction may be physically separated from the measuring junction, because often the transducer cannot be operated in close proximity to the measuring junction because it is located in machinery or similar hot, dirty environments. Thus, it is necessary to transmit the measurement signal over a certain distance.
When do I use a compensating cable?
Compensating cables are made of most cost-efficient substitute materials, which are not identical with the metal pair of the thermocouple. Therefore, they behave exactly the same as the thermocouple only within a certain measuring range. Compensating cables are used primarily for cost reasons due to their limited measuring range, as they are less expensive than thermocouple cables.
When do I use a thermocouple cable?
A thermocouple cable is made of the same material as a thermocouple, therefore the thermocouple cable also has the same physical properties and also the same application range as the thermocouple itself. Connecting the two wires at one end creates a thermocouple.
What do I have to pay attention to when insulating the compensating cable or the thermocouple cable?
In addition to the type of cable (i.e. whether a thermocouple cable or a compensating cable is used), the range of application of the cable also depends on the insulation material used for the cable and its properties. PVC, PFA, silicone or glass fiber are used. In addition to the area of application, the cables differ in other properties such as resistance to dust and moisture (IP class) and resistance to aggressive media. You will find the following cables in our product range:
-
Do I need a connector and what size should the connector be?
Thermocouples are either connected directly to the measuring device. However, it is much more common for thermocouples to be connected to the measuring device via a plug connection. At Testo Sensor, you will find the following connectors on offer:
-
How do you ensure the correct mechanical connection to the process?
Correct mechanical connection of the probe to the process ensures efficient, error-free and trouble-free measurement.
What length of protection sleeve do I need for my thermocouple?
For thermocouples with variable sheath length, please measure in advance what length you need. Each probe requires a minimum immersion depth to accept and correctly measure the temperature of the medium being measured. As a rule of thumb, the following advice can serve you: optimally, the immersion depth should correspond to 10 times the thermowell diameter, but at least a 5-fold value should be used.
Which sheath diameter should my thermocouple have?
Please consider what diameter you need: When measuring temperature in solids or when the probe is mounted in an immersion sleeve, the air surrounding the probe slows the conduction of heat from the medium to the probe. This also slows down the temperature measurement and, in extreme cases, leads to incorrect readings. Therefore, please make sure that the thermocouple is coupled to your measuring medium in the best possible way in terms of thermal technology, i.e. select the sleeve diameter so that the air gap is as small as possible.
We have provided more detailed information on mounting and immersion depths in the operating instructions, which you can download for each probe.
Which environmental influences is the thermocouple subject to?
Please also pay attention to whether you have certain requirements at the measuring point or in your process with regard to temperature, pressure, IP protection, steam or similar and compare your specification with our data sheets. If you have any questions or are unsure, please feel free to contact us.
What do I have to consider when mounting the cable thermocouple?
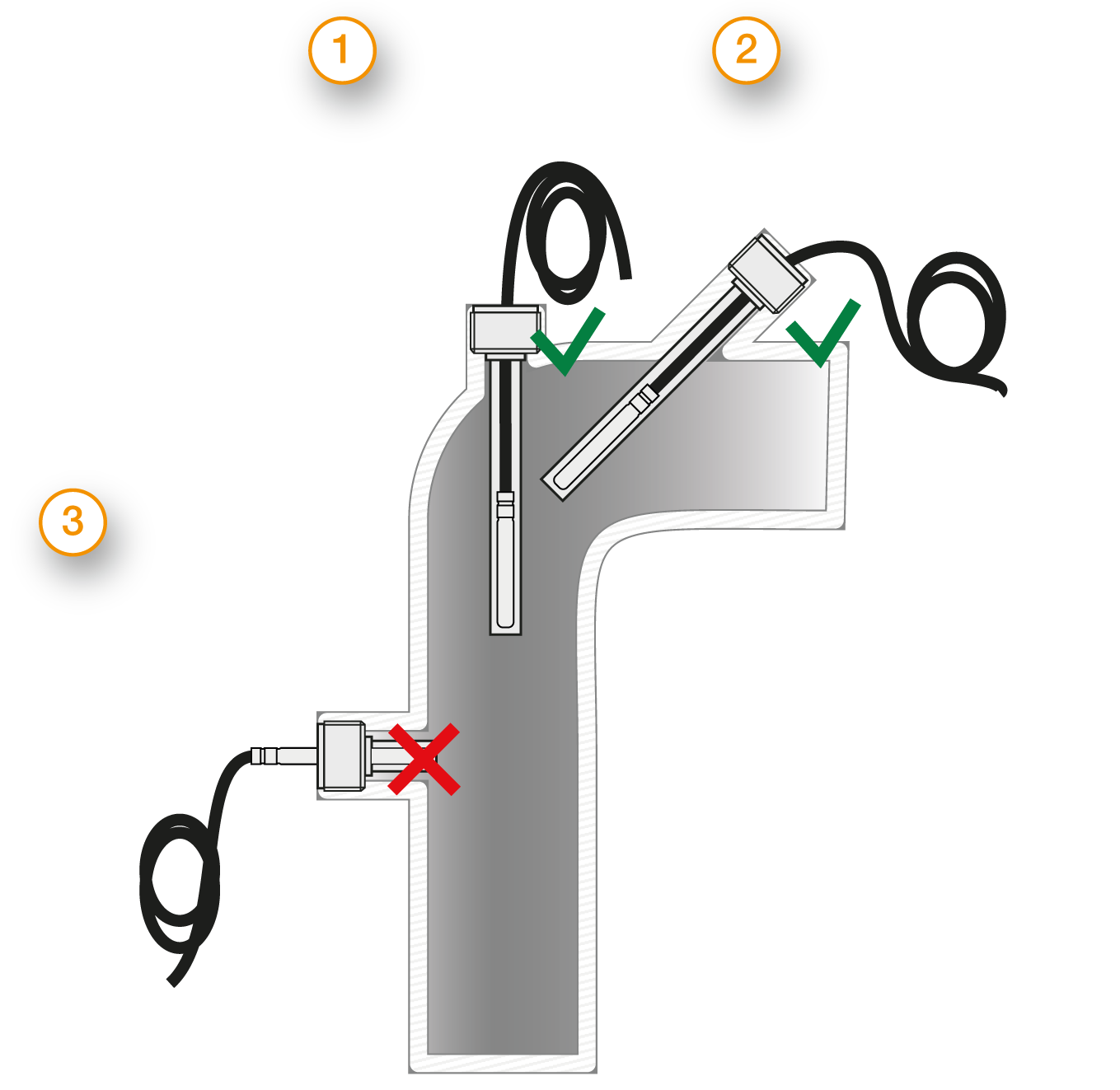 | Measurement errors can occur due to heat dissipation to the environment. To keep these as small as possible, we recommend immersing the protection sleeve of your temperature probe as deeply as possible in the medium to be measured during installation. The optimum installation depth should be 10-15 times the Ø of the protection sleeve or, when using an immersion sleeve, the Ø of the immersion sleeve. When installing in pipelines whose Ø does not have a sufficiently deep installation depth, you should install the probe either at an angle or in a pipe elbow. Make sure that there is sufficient space for the probe to be removed. 1) Installation with sufficient installation depth 2) Installation at an angle with small pipe Ø 3) Not like this: Minimum installation depth not reached |
| Installation by means of compression fitting: Please tighten the union nut of the compression fitting by hand as far as it will go (clearly noticeable). With a wrench matching the wrench size, please make a 1/4 turn on compression fittings with PTFE thrust collar. These compression fittings can be used several times in this way. In the case of compression fittings with stainless steel cutting ring, the compression fitting connects to the protection tube. This connection is pressure resistant up to 40 bar. However, the compression fitting can only be used once. It must also be tightened more firmly. Please tighten it with 1 3/4 turns. |
 | Mounting by using an immersion sleeve (4): Please note that the diameter and length of the immersion sleeve must be selected to suit the installation situation so that the minimum immersion depth can be achieved. Since the probe is not inserted directly into the medium, but via the immersion sleeve, the response times are somewhat slower. The probe should be selected in such a way that the protection sleeve touches the bottom of the immersion sleeve and that the air cushion around the protection sleeve is as small as possible. The use of thermal paste can improve the response times. |
| Please lay the cable with reserve loop (4) and in such a way that no water can penetrate the sensor head. This allows you to extend the probe without disconnecting the electrical connection. |
Which accessories do I need?
When placing your order, please consider whether you need any accessories. Please check the delivery details for each probe to see what is included in the scope of delivery.
We offer the following accessories:
Replacement of a defective thermocouple
When replacing a defective temperature probe, please pay close attention to which thermocouple you need, because the thermocouple types are not compatible with each other. Therefore, please refer to the technical data of the respective system to find out which Type has been installed. If the required information is not apparent in the operating instructions of the measuring device / equipment, the manufacturer of the machine or system should be contacted in case of doubt.
When the exact type of thermocouple has been determined, the mechanical adaptation must be tested. The temperature can only be measured correctly if the probe can be mounted correctly at the installation site. Otherwise, machines and equipment can easily malfunction.
Also make sure that you order thermal paste and mounting accessories such as compression fittings, cutting ring screw fittings or bayonet nipples if these also need to be replaced.
Frequently asked questions about temperature sensors
How much heat can cable thermocouples withstand?
The heat resistance of our probes depends on three components. In each case, the "weakest" part, determines how much heat the cable thermocouple can tolerate.
Protection sleeve
The stainless steel sleeve of the probe can withstand approx. 500 °C and is therefore not the critical component.
Thermocouple cable
We offer our cable thermocouples with four different cable materials, each suitable for different temperature ranges and IP protection classes.
- PFA: -50 °C to +260 °C (IP65)
- PVC -30 °C to +105 °C (IP65)
- Silicone: -50 °C to +180 °C (IP67)
- Glass fibre: -50 °C to +400 °C (IP20)
Thermocouple
Our thermocouples have different measuring ranges.
- Thermocouple type J: -40 °C to 750 °C in accuracy class 1
- Thermocouple type K: -40 °C to 1000 °C in accuracy class 1
More detailed information on the measurement curves, voltage tables, measuring ranges and accuracy classes can be found in the download area and on the respective product pages of the probes.
How do I check the function of a thermocouple?
The measurement curve of thermocouples is not linear. Therefore you need a special multimeter with an appropriate measuring input, which linearizes the signal and corrects the terminal point compensation at the same time, so that only the temperature measured at the measuring point is displayed.
Alternatively, you can check whether you can detect mechanical damage such as cable breakage or replace the thermocouple and see whether the error still occurs.
How can I tell that my thermocouple is defective?
The thermocouple shows strange values? Or it does not show any values? This behavior may be a sign that your sensor is defective or that it has not been connected correctly.
To find out if there is a defect, you can use a multimeter with an appropriate connection for thermocouples to check if the correct voltage has been reached.
Alternatively, you can test on a trial basis to see if a replacement will remedy the situation.
How do I connect the thermocouple correctly?
When connecting, please make sure that you follow our wiring diagrams and voltage tables. As connection variants we offer mini TE connectors (miniature connectors) and TE connectors (standard connectors) according to DIN EN 60584 color coding or open wire ends. You will find the necessary information in the operating instructions of your probe.
How can I protect the cable thermocouple from environmental influences?
We offer suitable immersion sleeves in our online store to protect the thermocouple. You will also always find the matching accessories for your probe in the respective operating instructions.
For easier orientation, we have always indicated suitable accessories in the respective operating instructions / data sheet of the temperature probe.