With the average value transmitter, the temperature measurement signal can be transmitted safely, easily and over long distances to the controller or the systems.
You will find the most important information in the following guide
- What is a transmitter?
- What are average value transmitters and what are they used for?
- What types of average value transmitters are there and what are the differences between them?
- What are the advantages of average value transmitters compared to other types of transmitter systems?
- What features and specifications should be considered when selecting an average value transmitter?
What is a transmitter?
They are also referred to as transmitters, transducers, signal converters or simply converters. They are used to convert physical measured variables such as temperature, humidity, differential pressure etc. into standardized electrical signals.
In the case of a temperature transmitter, the measured variable to be converted is temperature.
The input signal is a resistance value for resistance-based temperature probes and a voltage value for thermocouples. The output signal is usually either 0 ... 10 V or 4 ... 20 mA. Historically, however, there are also 0-1 V / 0-5 V or 0-20 mA signals.
What are average value transmitters and what are they used for?
Average value transmitters are used in ventilation ducts where they measure the temperature in gaseous media and output this as a standardized signal (4 - 20 mA or 0 - 10 V).
Average value transmitters measure the temperature over the entire length of their rod. Please place the transmitter in the air duct at equal distances and maintain a bending radius of at least 35°. Fasten the rod with mounting clips (included). You can find mounting flanges made of aluminum, plastic or stainless steel as well as compression fittings, mounting clamps and capillary tube feedthroughs on our website. Please lay the cable with a spare loop. This allows you to extend the probe without disconnecting the electrical connection.
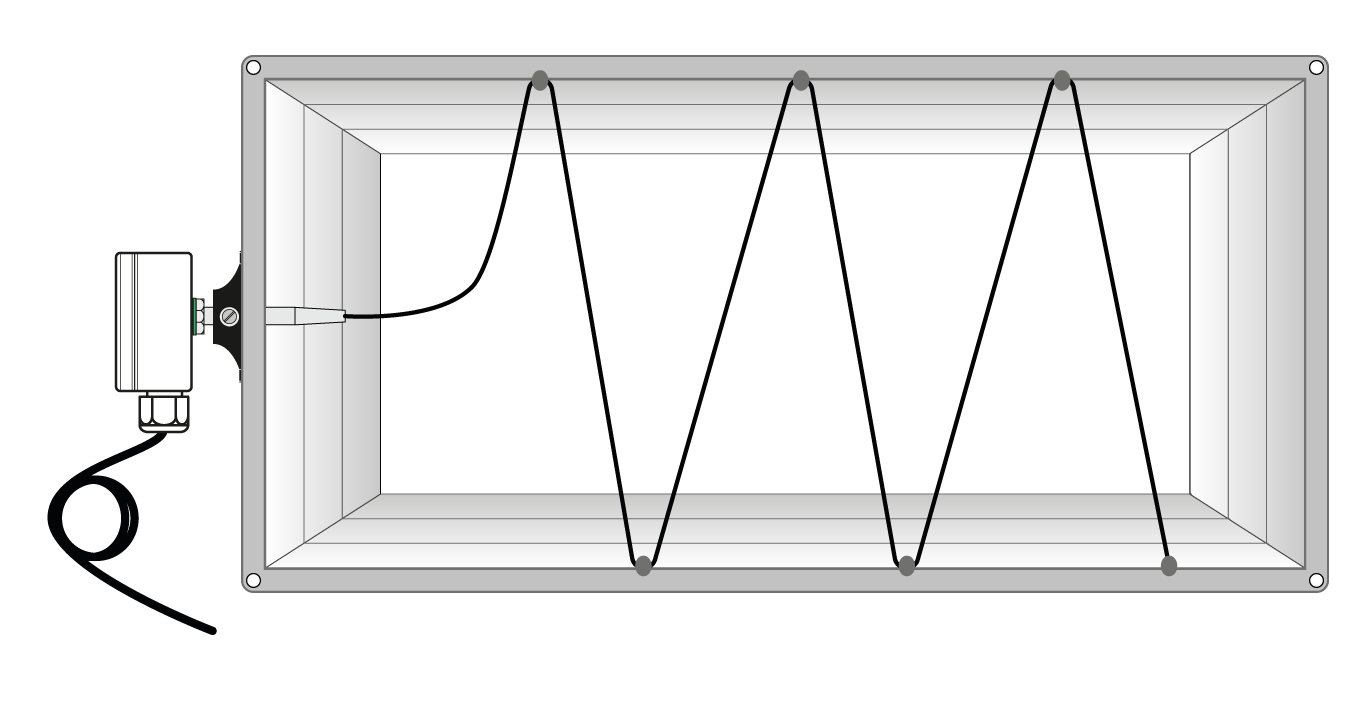
What types of average value transmitters are there and what are the differences between them?
There are different types of average value transmitters. We offer our average value transmitters with thermoplastic, standard variant and as a variant with display, each with 4-20 mA and 0-10 V output.
The Pt1000 class B sensor is installed in the active temperature probes and you can choose between an output of 4 to 20 mA or 0 to 10 V.
Configuration of the articlels
We offer the following rod lengths for our average value transmitters:
0-4 m, 3 m, 6 m
What are the advantages of average value transmitters compared to other types of transmitter systems?
Average value temperature transmitters have many advantages, such as accurate measurement, easy installation and integration into existing systems, high durability and reliability.
What features and specifications should be considered when selecting an average value transmitter?
Factors such as measuring range, output signal, power supply and environmental conditions should be considered when selecting an outdoor transmitter. With our DIP switches you have a choice of eight measuring ranges. The Pt1000 class B sensor is used for temperature measurement.
We offer a 0-10 V voltage output and a 4-20 mA current output. The ambient temperature of the transmitter is between -30 °C and +70 °C. The voltage supply is 24 V AC ⁄ DC (± 10 %) for the voltage version and 15 - 36 V DC for the current version.